Electric compressors feature two distinct connectors designed for specific purposes:
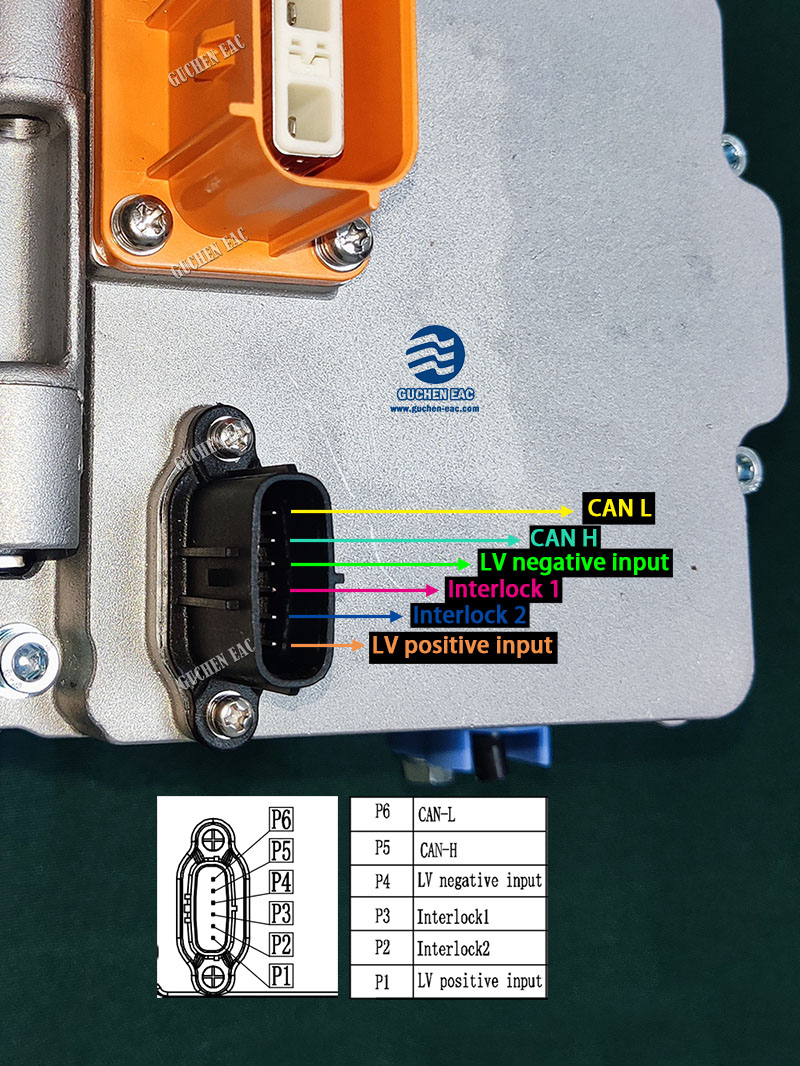
1. Low-Voltage Connector (6-8 Pins)
The low-voltage connector serves as the control interface. It typically includes:
- Power Supply (24V or 12V): Positive and ground pins ensure stable power for the control circuitry.
- CAN Communication Lines (CAN L and CAN H): These pins facilitate data exchange between the compressor and the vehicle's air conditioning controller. CAN (Controller Area Network) enables real-time monitoring and command transmission, ensuring the compressor operates efficiently and in sync with other vehicle systems.
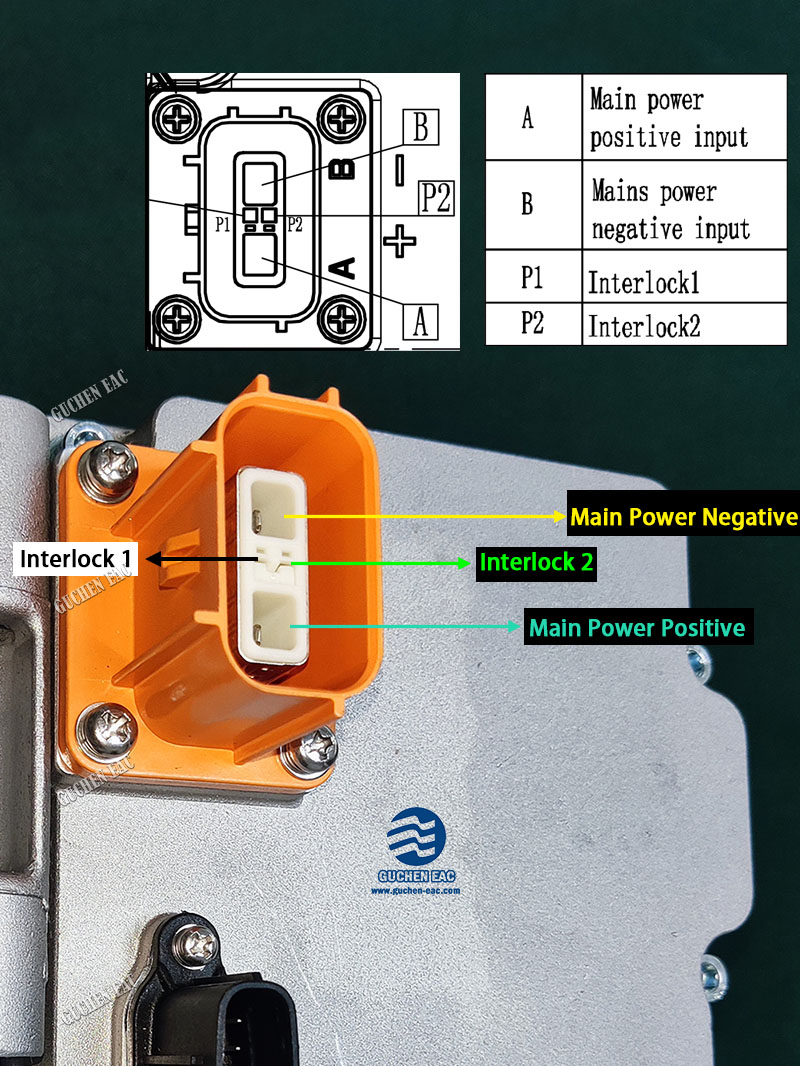
2. High-Voltage Connector (2 Pins + Interlock)
- Power Pins: High-voltage positive and negative pins supply the energy required for compressor operation.
- High-Voltage Interlock (HVIL) pin: This safety feature ensures proper connection and prevents accidental engagement of the high-voltage system, enhancing operational safety. The inclusion of HVIL and the separation of low- and high-voltage functions underscore the emphasis on safety in modern electric compressor design. Proper handling, installation, and maintenance of these components are vital to avoid hazards.
Once the vehicle's pre-charging process is completed, power is supplied to both the high- and low-voltage sides of the compressor. However, whether the compressor operates is determined by commands sent via CAN communication by the air conditioning controller.
Related Reading:
Research on Control Strategies for Electric Compressors in Electric Vehicles