In response to reader feedback from our previous article on
BYD’s thermal management system, which mentioned that the Xiaomi SU7 adopts a 9-way valve, today we will take a closer look at the thermal management system of the Xiaomi SU7 to understand its actual configuration.
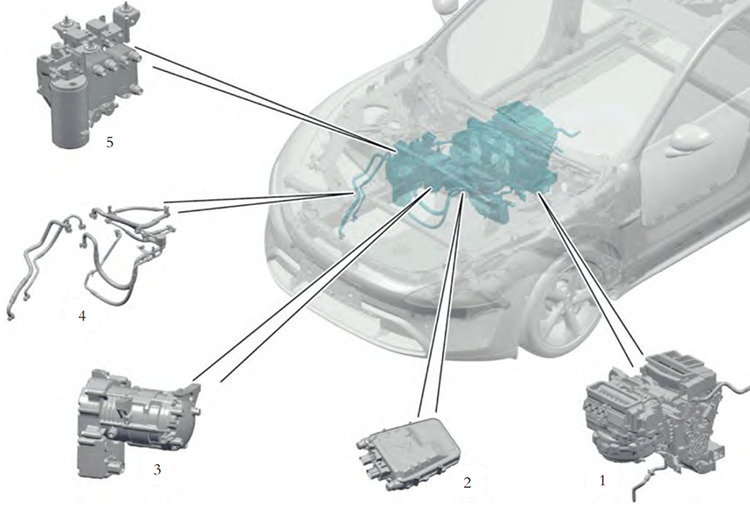
The primary function of a thermal management system is to regulate the cabin temperature for occupant comfort, while also controlling the temperature of key components such as the battery, motor, and controller under various environmental conditions and operating states. The image below shows the main components of the SU7 thermal management system and their installation locations in the actual vehicle.
▲Figure: Main Components of the Xiaomi SU7 Thermal Management System
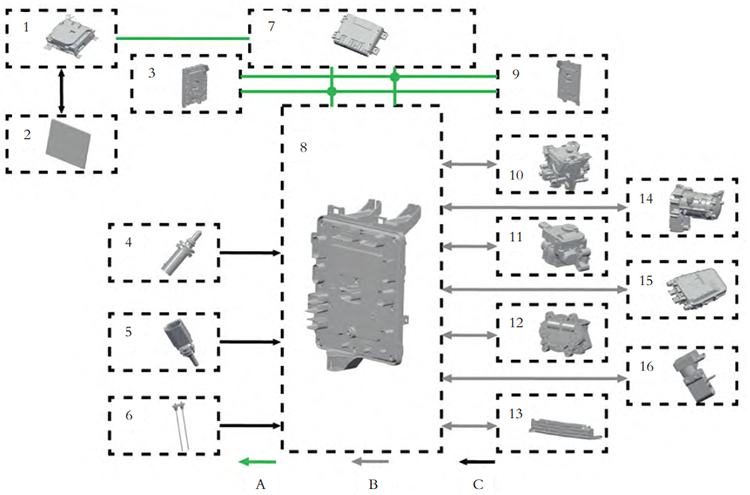
The following diagram illustrates all the components involved in the thermal management system and their control pathways. The system includes the front, left, and right zone controllers, the intelligent cockpit domain controller, and the central vehicle domain controller.
▲Figure: Xiaomi SU7 Thermal Management System: Key Components and Control Links
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
| Intelligent Cockpit Domain Controller |
Central Display Screen |
Left Zone Controller |
Water Temperature Sensor |
Ambient Temperature Sensor |
Liquid Level Sensor |
Central Vehicle Domain Controller |
Front Zone Controller |
| 9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
| Right Zone Controller |
Water Circuit Integration Module Assembly |
3-Way Water Valve |
9-Way Water Valve |
Active Air Intake Grille |
Electric Compressor Assembly |
High-Voltage PTC Heater Assembly |
Electronic Expansion Valve |
| A |
B |
C |
| CAN Bus |
LIN Bus |
Hardwired Signals |
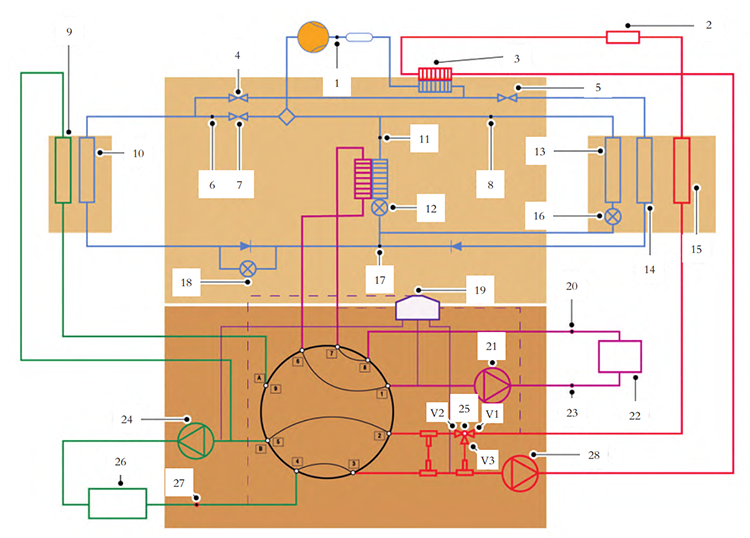
From the diagram, it is evident that Xiaomi’s thermal management system is highly integrated. By incorporating flow control components such as the 9-way and 3-way water valves, the system is capable of managing multiple operating scenarios. The detailed thermal management system circuit is shown in the figure below.
▲Figure: Thermal Management System Circuitry of the Xiaomi SU7
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
| Refrigerant Outlet Temperature Sensor (Compressor) |
High-Voltage PTC Heater |
Heat Exchanger |
Shutoff Valve |
Shutoff Valve |
Refrigerant Temperature Sensor |
Shutoff Valve |
| 8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
| Refrigerant Temperature Sensor |
Radiator |
Condenser |
Refrigerant Temp & Pressure Sensor |
Expansion Valve |
Evaporator |
Bypass Line |
| 15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
| Heater Core |
Expansion Valve |
Refrigerant Temp & Pressure Sensor |
Expansion Valve |
Reservoir |
Water Temperature Sensor |
Water Pump |
| 22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
| Power Battery Pack |
Water Temperature Sensor |
Water Pump |
3-Way Valve |
Electric Drive System |
Water Temperature Sensor |
Water Pump |
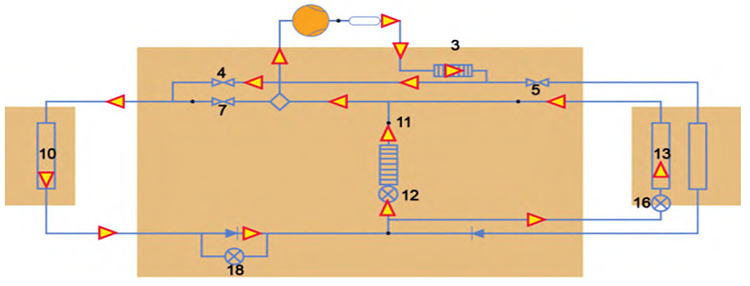
Operating Modes of the Thermal Management System:
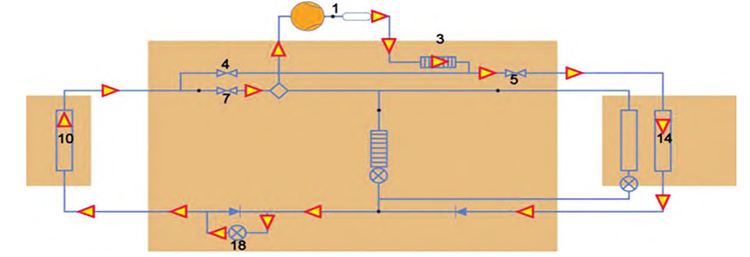
1. Heat Pump Mode
When the ambient temperature is not too low, the
air conditioning compressor operates in heat pump mode. For example, when cabin heating is required, the system opens shutoff valves 5 and 7, and closes valve 4. The high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor flows through heat exchanger 3, transferring heat to the cabin heating loop. After heat exchange, the refrigerant passes through line 14, undergoes expansion via expansion valve 18, and becomes low-temperature, low-pressure gas. It then releases the cold to the ambient air via radiator 10 before returning to the compressor.
▲Figure: Heat Pump Mode
2. Cooling Mode
In cooling mode, shutoff valves 5 and 7 are closed while valve 4 is open. The high-pressure refrigerant from the compressor passes through 3 and 4, then enters condenser 10 for heat rejection. It is then sent through expansion valve 16 and the evaporator, before returning to the compressor. If the battery requires cooling, expansion valve 12 opens, allowing refrigerant to pass through the heat exchanger and lower the coolant temperature of the battery circuit.
▲Figure: Cooling Mode
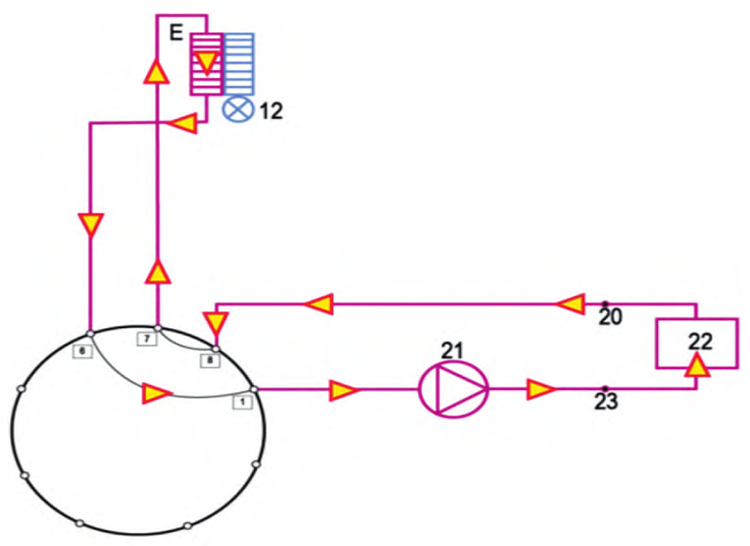
3. Battery Cooling Mode
Depending on ambient and battery temperature, the thermal management system adjusts the appropriate cooling circuit via the 9-way valve. Coolant driven by electric pump 21 flows through the power battery 22, absorbing heat. It then passes through the heat exchanger to transfer the heat to the refrigerant, and returns through the 9-way valve to complete the cooling loop.
▲Figure: Battery Cooling Mode
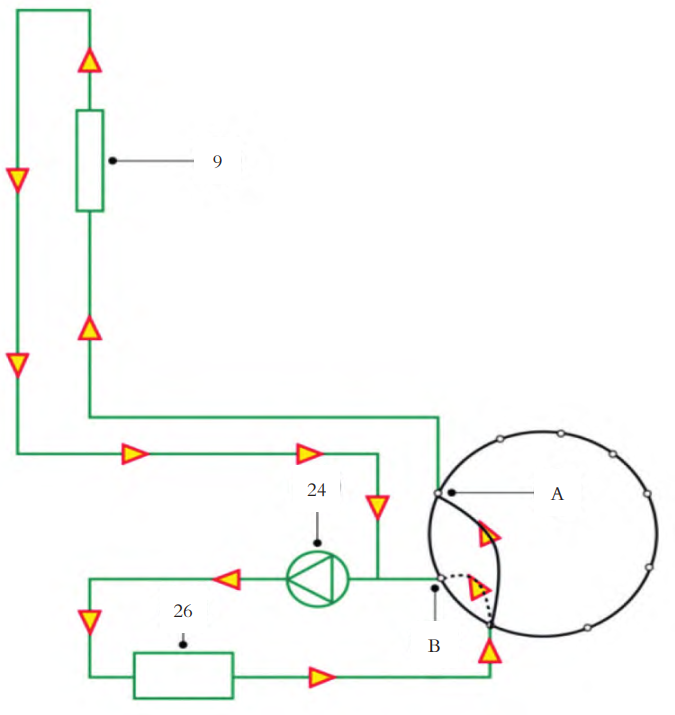
4. Motor Cooling Mode
There are several cooling strategies for the electric drive system. One common approach is cooling through the radiator. Water pump 24 drives coolant through the electric drive system 26 and into the 9-way valve, which allocates flow between branches A and B based on cooling demand. The A-branch coolant flows through radiator 9 for cooling, and then merges with the B-branch coolant before returning to the pump.
▲Figure: Motor Cooling Mode
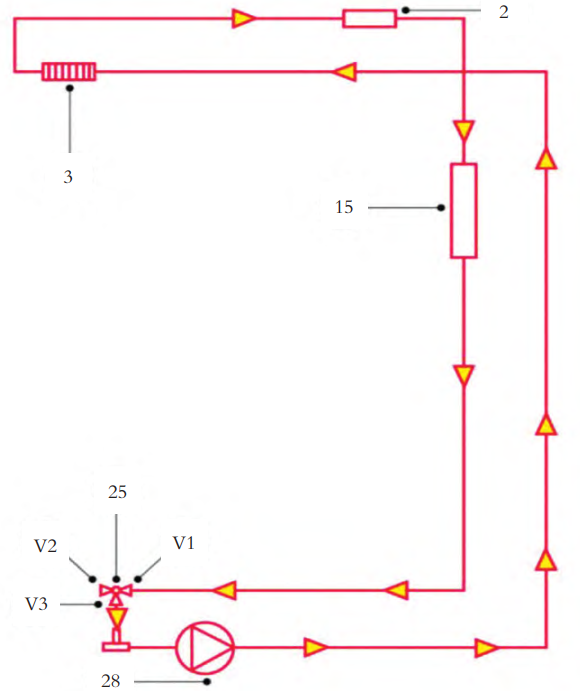
5. Cabin Heating Mode
There are two primary methods for cabin heating. The first involves transferring heat from the refrigerant to the coolant via heat exchanger3, which then delivers the heat to the passenger compartment. The second method uses the high-voltage heater 2 to directly heat the coolant, which then transfers thermal energy to the cabin. The selection of the heating mode depends on the ambient temperature. Driven by water pump 28, the coolant first flows through heat exchanger 3, then passes through the high-voltage heater 2. The heated coolant delivers thermal energy to the cabin via heater core 15 before returning to the inlet of the water pump to complete the cycle.
▲Figure: Cabin Heating Mode